Revolutionary cloud computing is a crucial upriser in advanced data management, a primary aspect of health tech in medical data archiving. It not just safeguards data but categorically adds efficiency to storing large datasets. The key storage types? Cold Storage, Hot Storage, and Immutable Storage. With unique features tailored to specific data retention needs, understanding the data storage type ensures top suitability, cost-effectiveness and robust data protection. This also emphasizes the urgency to adopt innovative cloud archival solutions to retain and secure critical data, especially for thriving healthcare data archival.
Let’s find out more about each storage type!
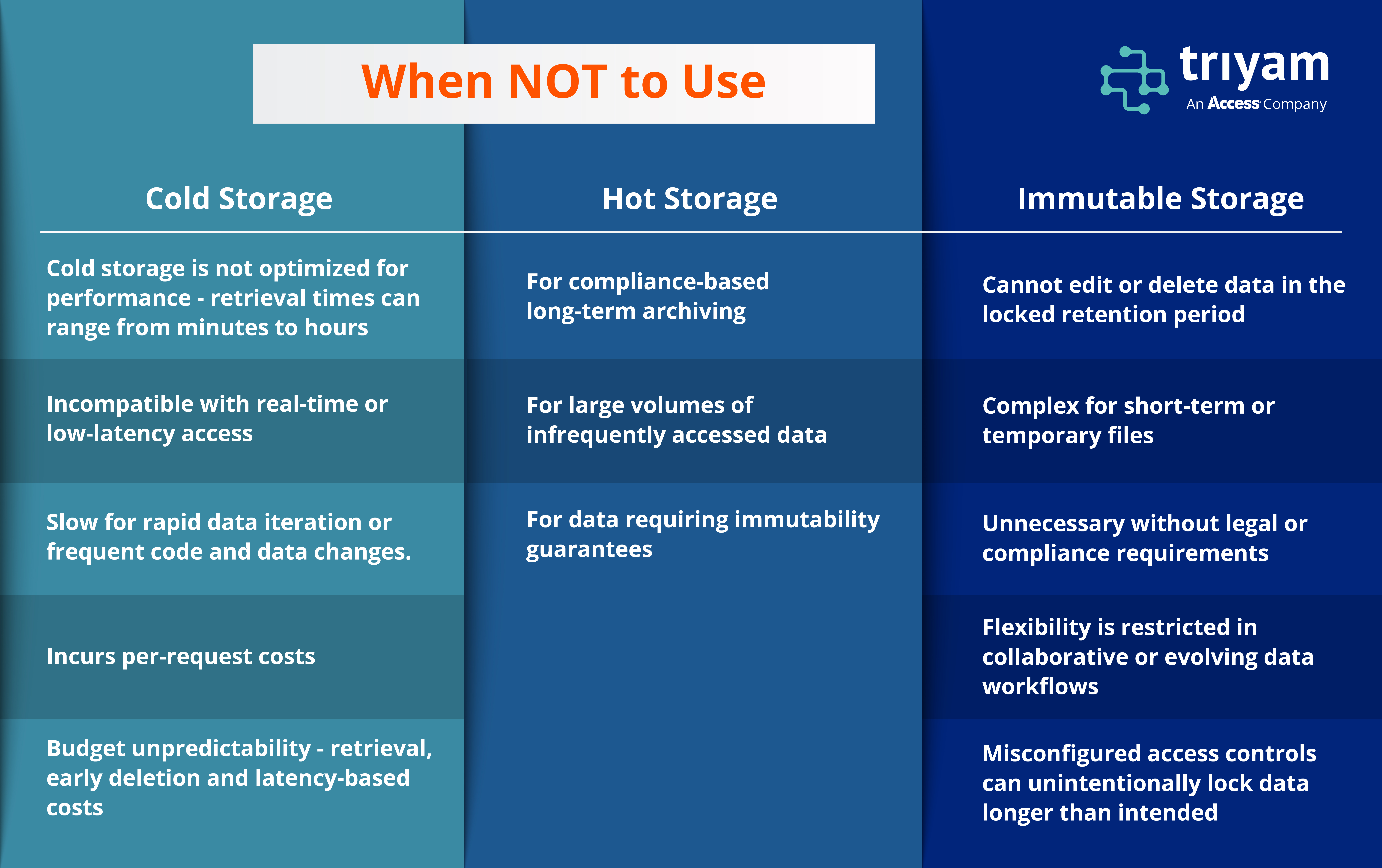
Cold Storage/Glacier Storage
Cold storage refers to a class of cloud storage designed for data that is infrequently accessed but must be retained for long periods. Glacier Storage, a term popularized by Amazon Web Services (AWS), is a prime example of this category.
As per Grand View Research, the global cold storage market was valued at $159.7 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 18.1% from 2025 to 2030, reaching an estimated $427.6 billion by 2030.
Key Features:
- Cost-effective
- Long-term retention
- Scalable
Benefits:
- Significant savings on storage expenses.
- Meets compliance standards and regulatory data retention mandates.
- Ensures high data durability with multiple redundancy levels.
- Seamlessly scales to handle increasing data volumes.
- Supports sustainable data management practices.
Enhancement Strategies:
- Lifecycle Policies: Automate data transitions after a defined period.
- Regular Data Audits: Periodically review to ensure relevance and compliance.
- Integrate with Plan B: Backup strategies ensure comprehensive data protection.
- Monitor Access Patterns: Analyze access logs to optimize data storage tiers.
- Ensure Data Encryption: Encrypt data for protection at rest and during transfer.
Hot Storage
Unlike cold storage, hot storage is a high-performance cloud storage tier designed for frequently accessed and time-sensitive data for instant retrieval. It is ideal for workloads requiring real-time read/write functionality, mainly for operational or transactional data.
A 2024 IDC report notes 80% of enterprise data is hot or active within the first 30 days of creation, but only 10-15% remains hot after 90 days. This resonates with the prominence of cloud-smart tiering strategies.
Key Features:
- High Availability
- High Throughput
- Low Latency Access
- Optimized for Performance
- Integration Friendly
Benefits:
- Immediate real-time access to mission-critical data.
- Ideal for active workloads such as running web applications, databases, and analytics platforms.
- Optimized for rapid data retrieval and seamless read/write operations.
- Automatically scales with workload demand.
- Easily integrates with cloud-native services.
Enhancement Strategies:
- Implement Caching for Frequent Queries: Offload repeated data access.
- Monitor Usage Patterns: Continuously analyze data access trends to optimize storage tiering and costs.
- Lifecycle Management: Automate to move inactive data to archival tiers.
- Compression and Deduplication: Streamline storage footprint.
- Use Object Versioning Wisely: Turn on versioning to prevent accidental data loss but prune older versions to control costs.
Immutable Storage
Immutable cloud storage prevents data from being deleted or altered for a specified retention period, ensuring data integrity and protection against unauthorized changes.
93% of IT leaders support immutable storage for protecting backup data against ransomware attacks and 69% consider it essential for corporate cybersecurity strategies, signifying Zero Trust Data Resilience (ZTDR) practices.
Key Features:
- Write Once, Read Many (WORM)
- Retention Policy Setting
- Compliance Support
Benefits:
- Protects against ransomware and malicious alterations.
- Adheres to legal and regulatory data retention requirements.
- Ensures data authenticity and accuracy.
- Facilitates easy retrieval of unaltered data for audits.
- Ensures critical data remains unchanged and accessible.
Enhancement Strategies:
- Define Clear Retention Periods: Enforce data retention policies.
- Regularly Review Policies: Updated policies meet evolving standards.
- Integrate with Backup Systems: Backup solutions offer layered protection.
- Monitor Access Logs: Track access logs to detect unauthorized accesses.
- Educate Stakeholders: Relevant personnel must adhere to immutability policies.
Connect with Triyam for detailed cloud-archival strategies!