When healthcare data is deleted, it can commonly be expected to be removed forever. Consequently, the desired data to be retained is expected to be saved forever. Reality can be different.
Deleted data survive in backups, logs or even shadow IT systems – proper purging is essential for complete clearance. Negligence and overdoing data retention can violate compliance checks and incur consequences.
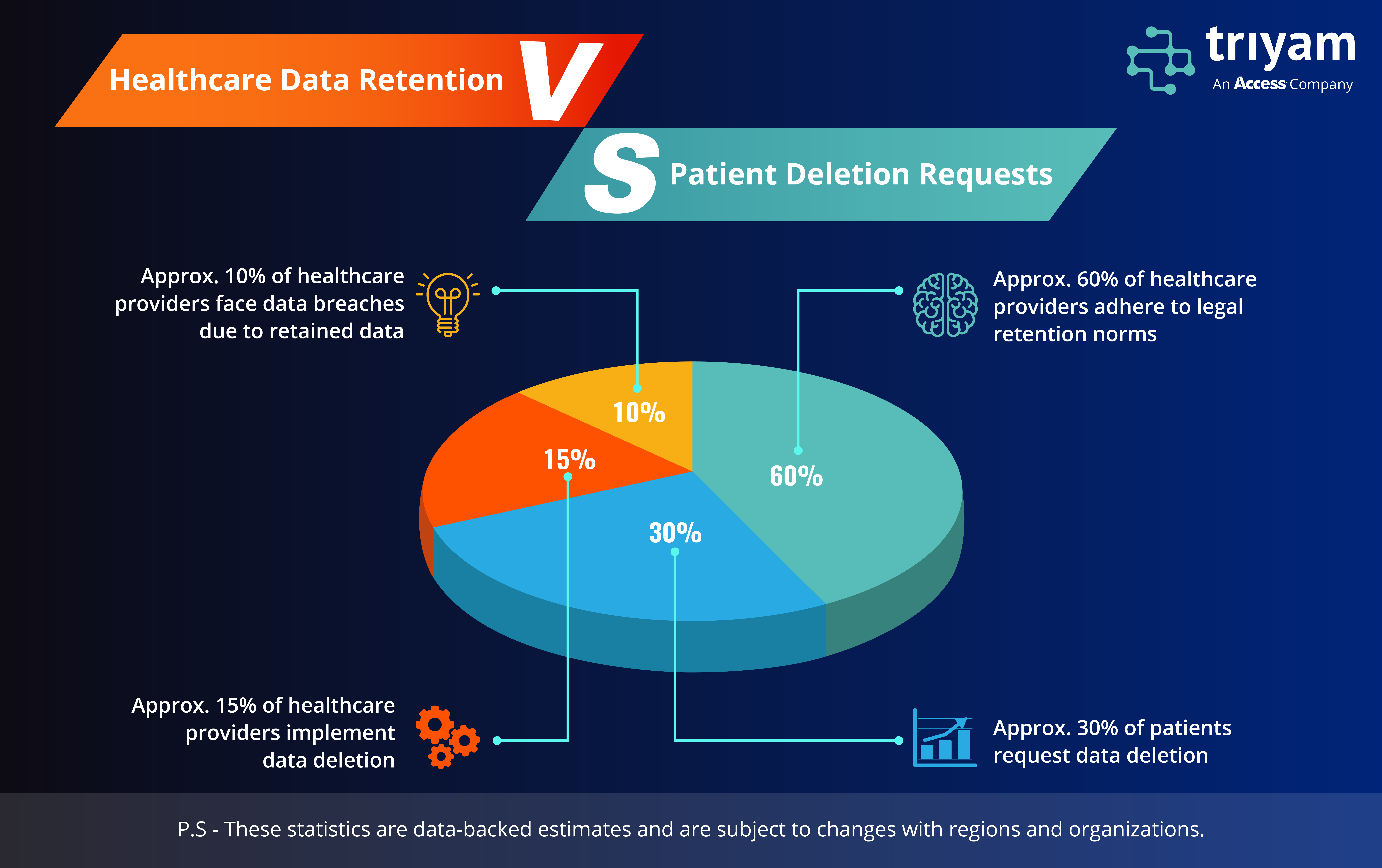
Amidst rising significance of patient rights to control personal data, including the ability to request deletion, healthcare providers face legal obligations to retain relevant medical records for extended periods and eliminate the unrequired, creating a complex landscape where patient rights and legal requirements intersect. A sound understanding of what and why data should be deleted, to not interfere with critical clinical details that need to be preserved, is of prime importance.
How Patient Autonomy and Legal Mandates Overlap
- Patient Rights to Data Deletion: Privacy concerns and control rights can cause deletion requests.
- Legal Retention Requirements: Healthcare providers are mandated by law to retain medical records for specific periods, as per regions and the nature of data.
- Contradiction: Patient requests for data deletion may conflict with legal retention standards, posing ethical and operational challenges for healthcare providers.
- Conditional Deletion Frameworks: Some healthcare regulations allow partial or conditional deletion, where identifiable patient data can be anonymized or de-identified to balance privacy rights with retention laws. This middle ground is often used in research or archival contexts.
- Consent and Transparency Obligations: Healthcare providers must ensure patients are fully informed about compliant data use, retention, and deletion policies during consent, to abide by legal mandates and address patient requests.
Legal Frameworks Governing Data Retention
- HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act): While HIPAA does not specify a retention period for medical records, it requires covered entities to retain certain documents for six years.
- State Laws: Individual states have their own laws governing the retention of medical records. For example, in California, physicians are required to retain records for 10 years after the last patient visit. Medical records retention is governed by state-specific laws, which can vary.
- GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation): GDPR grants EU individuals the right to request the deletion of personal data. However, exceptions exist, such as when data retention is necessary for compliance with legal obligations.
Challenges in Striking a Balance
- Operational Complexity: Healthcare providers need to navigate the complexities of complying with both patient requests and legal obligations, often requiring legal counsel and policy adjustments.
- Data Management Systems: Updating data management systems is crucial to ensure reliant data deletion requests, adhering to evolving compliance.
- Ethical Considerations: Providers must consider the ethical implications of retaining data that patients wish to be deleted.
- Cross-Jurisdictional Regulations: Healthcare organizations operating across regions must manage varying data privacy and retention laws (e.g., HIPAA in the U.S. vs. GDPR in the EU), which can complicate standardization of data policies and lead to compliance gaps.
- Resource Constraints: It’s a complicated weave of nuanced data governance strategies with significant investment in staff training, technology upgrades, and ongoing audits.
Key Points to Keep a Tab Of
- Risk of Non-Compliance: Failure to adhere to legal retention requirements can result in legal penalties, loss of accreditation, and damage to reputation.
- Resource Allocation: Managing data retention and deletion requests requires dedicated resources, including legal and IT experts.
- Policy Development: Healthcare providers must develop clear policies that address data retention and deletion, ensuring transparency and consistency in handling such requests.
Strategic Approaches to Check Complexity
- Clear Communication: Data deletion and retention policies, to-dos and best practices should be clearly conveyed to patients, ensuring they understand their rights and the reasons for data retention.
- Regular Audits: Conducting regular audits and monitoring data management practices helps identify data that can be deleted and information that needs to be preserved as per compliant frameworks.
- Staff Awareness: Healthcare professionals must be thorough and data-backed in their legal knowledge so that they do not misinform patients or conduct noncompliant data deletion and data retention practices.
- Legal Consultation: Engaging legal counsel can provide guidance on navigating the complexities of data retention laws and patient rights.
- Tech Tools: Advanced data management systems streamline the process of handling data retention and deletion requests with innovative features of compliance and security, ensuring efficiency.
By understanding the legal frameworks, patient mentality, privacy factors, data value, addressing operational complexities and implementing effective strategies, healthcare leaders can channel through the complex intersection, be compliant and elevate patient trust.
Connect with Triyam for a tailored data retention walkthrough!